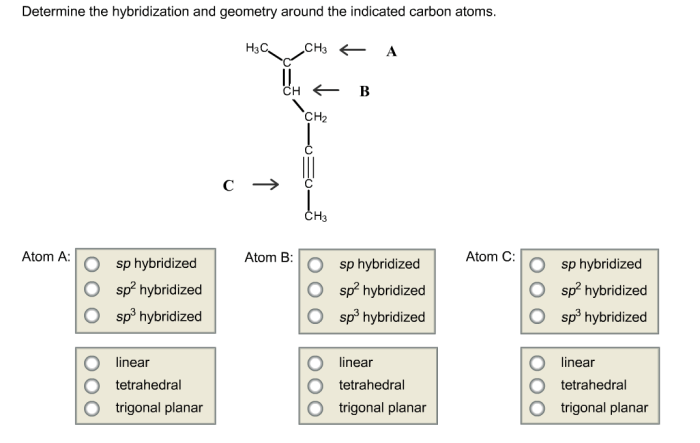
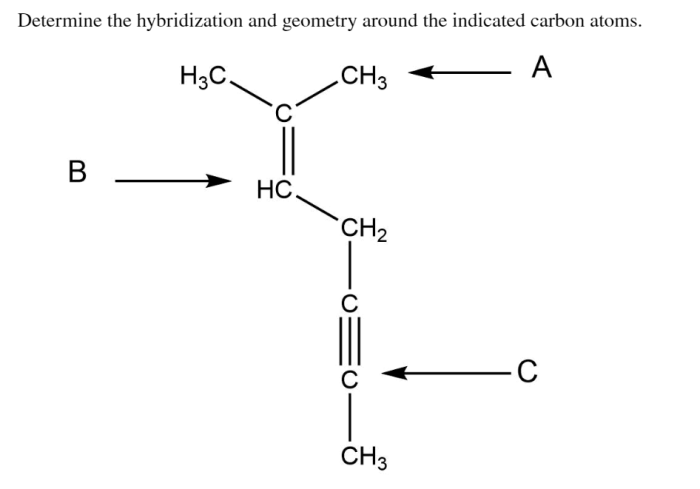
Determine the hybridization and geometry around the indicated carbon atoms. – Embarking on a journey to understand hybridization and geometry around carbon atoms, this exploration unveils the fundamental principles governing molecular structure. Hybridization, a cornerstone of chemistry, dictates the spatial arrangement of atoms within a molecule, profoundly influencing its properties and behavior.
Delving into the intricacies of carbon atom hybridization and geometry, this discourse elucidates the concepts, techniques, and applications that empower chemists to decipher the molecular architecture of the world around us.
1. Hybridization of Carbon Atoms: Determine The Hybridization And Geometry Around The Indicated Carbon Atoms.
Hybridization is a fundamental concept in chemistry that describes the mixing of atomic orbitals to form new hybrid orbitals with different shapes and energies. It plays a crucial role in determining the molecular geometry and properties of compounds, particularly those containing carbon.
Types of Hybridization, Determine the hybridization and geometry around the indicated carbon atoms.
- sp Hybridization:Two atomic orbitals (one s and one p) combine to form two sp hybrid orbitals, which are linear in shape and oriented 180° apart.
- sp2Hybridization: Three atomic orbitals (one s and two p) combine to form three sp 2hybrid orbitals, which are trigonal planar in shape and oriented 120° apart.
- sp3Hybridization: Four atomic orbitals (one s and three p) combine to form four sp 3hybrid orbitals, which are tetrahedral in shape and oriented 109.5° apart.
2. Molecular Geometry around Carbon Atoms
The hybridization of carbon atoms directly influences the molecular geometry around them. The shape of the molecule is determined by the arrangement of the electron pairs in the hybrid orbitals.
Molecular Geometries
- Linear:sp hybridized carbon atoms form linear molecules with a bond angle of 180°.
- Trigonal Planar:sp 2hybridized carbon atoms form trigonal planar molecules with bond angles of 120°.
- Tetrahedral:sp 3hybridized carbon atoms form tetrahedral molecules with bond angles of 109.5°.
3. Determining Hybridization and Geometry
Determining the hybridization and geometry around a carbon atom involves several steps:
Molecular Orbital Theory
Molecular orbital theory can be used to predict the hybridization of carbon atoms based on the number of electron pairs in the valence shell.
Experimental Techniques
Experimental techniques such as X-ray crystallography and NMR spectroscopy can be used to determine the molecular geometry of compounds, which can then be used to infer the hybridization of the carbon atoms.
4. Applications of Hybridization and Geometry
Understanding hybridization and geometry is crucial in chemistry for several reasons:
Molecular Properties
Hybridization and geometry affect molecular properties such as bond length, bond strength, and reactivity.
Applications
Knowledge of hybridization and geometry is essential in fields such as drug design and materials science.
FAQ Overview
What is the significance of hybridization in determining molecular geometry?
Hybridization dictates the spatial arrangement of electron pairs around an atom, which in turn determines the molecular geometry. By understanding hybridization, chemists can predict the shape and bonding characteristics of molecules.
How can experimental techniques be used to determine molecular geometry?
Techniques such as X-ray crystallography and NMR spectroscopy provide experimental evidence for molecular geometry. These techniques allow chemists to measure bond lengths, angles, and other structural parameters, confirming the predicted hybridization and geometry.