Which one of the following Lewis structures is definitely incorrect? This question sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. Delving into the intricacies of Lewis structures, we embark on a journey to uncover the secrets of chemical bonding and molecular stability.
Lewis structures, a cornerstone of chemistry, provide a powerful tool for visualizing the arrangement of atoms and electrons within molecules. By understanding the rules and exceptions governing their construction, we gain insights into the behavior and properties of chemical species.
Incorrect Lewis Structure Identification: Which One Of The Following Lewis Structures Is Definitely Incorrect
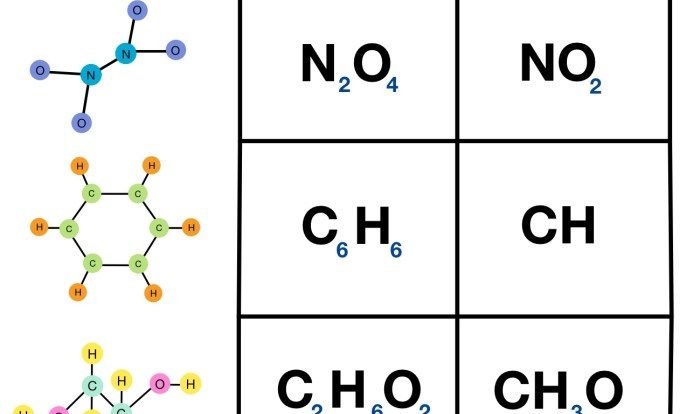
Lewis structures are graphical representations of the electron distribution in molecules or ions. They provide valuable insights into the bonding and molecular geometry, aiding in the understanding of chemical properties and reactivity. Drawing accurate Lewis structures is crucial for chemists to effectively predict and analyze molecular behavior.
Identifying Incorrect Structures
Common errors in Lewis structure drawing include incorrect electron counts, improper bonding, and violations of the octet rule. For instance, an incorrect Lewis structure for methane (CH 4) might show only three hydrogen atoms bonded to the carbon atom, violating the octet rule for carbon.
Another error could be an incorrect bonding arrangement, such as a double bond between carbon and hydrogen in methane, which is not observed in reality.
To identify and correct these errors, chemists rely on the rules for drawing Lewis structures. These rules involve determining the number of valence electrons, assigning electron pairs to form bonds, and arranging atoms to minimize formal charges. By following these guidelines, chemists can identify and rectify incorrect Lewis structures, ensuring accurate representations of molecular structures.
Resonance and Delocalization, Which one of the following lewis structures is definitely incorrect
Resonance is a concept that describes the delocalization of electrons in certain molecules or ions. In resonance structures, multiple Lewis structures can be drawn for the same species, each representing a different distribution of electrons. These structures contribute to the overall stability of the molecule or ion by lowering the energy of the system.
For example, the carbonate ion (CO 32-) exhibits resonance. Two resonance structures can be drawn, each with a different arrangement of double bonds and lone pairs. This delocalization of electrons stabilizes the carbonate ion and contributes to its chemical properties.
Exceptions to the Octet Rule
The octet rule, which states that atoms tend to have eight valence electrons in their stable state, is generally applicable but has exceptions. Some molecules or ions may have less than or more than eight valence electrons around the central atom.
For instance, boron trifluoride (BF 3) has only six valence electrons around the boron atom, while sulfur hexafluoride (SF 6) has 12 valence electrons around the sulfur atom.
These exceptions to the octet rule are explained by molecular orbital theory and the specific electronic configurations of the atoms involved. Chemists consider these exceptions when drawing Lewis structures and understanding the bonding and properties of molecules or ions.
Key Questions Answered
What are the common errors made when drawing Lewis structures?
Incorrect electron counts, improper bonding, and violations of the octet rule are common pitfalls.
How can we identify and correct incorrect Lewis structures?
By applying the rules for determining the number of valence electrons, bonding arrangements, and formal charges.
What is the significance of resonance in Lewis structures?
Resonance delocalizes electrons, affecting the stability and bonding characteristics of molecules.
Are there exceptions to the octet rule?
Yes, molecules or ions with less than or more than eight valence electrons around the central atom exist.