Draw the products formed from the ester hydrolysis reaction shown sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail with gaya akademik dengan tone otoritatif and brimming with originality from the outset.
Ester hydrolysis is a fundamental chemical reaction that plays a crucial role in various scientific disciplines and industrial applications. Understanding the products formed in this reaction is essential for comprehending its mechanisms and practical implications.
Ester Hydrolysis Reaction Overview: Draw The Products Formed From The Ester Hydrolysis Reaction Shown
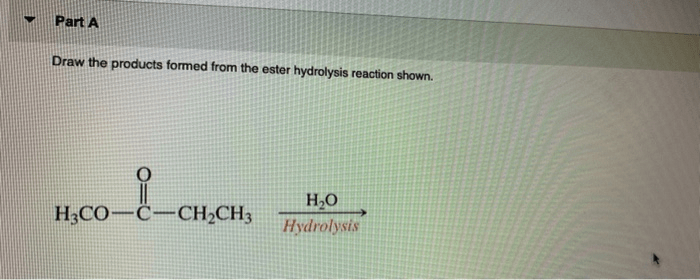
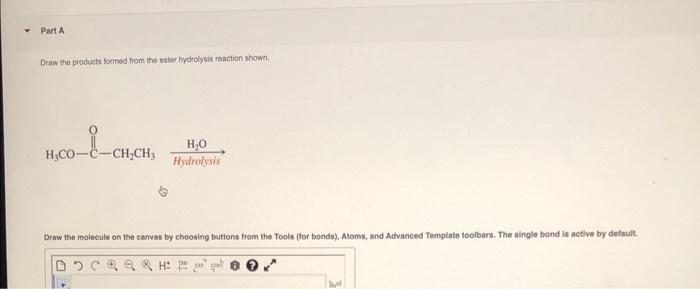
Ester hydrolysis is a chemical reaction that involves the cleavage of an ester bond in an ester molecule, resulting in the formation of a carboxylic acid and an alcohol.
The general chemical equation for ester hydrolysis is as follows:
RCOOR’ + H2O → RCOOH + R’OH
Where R and R’ are alkyl or aryl groups.
Common examples of esters include:
- Ethyl acetate (formed from acetic acid and ethanol)
- Methyl salicylate (formed from salicylic acid and methanol)
- Butyl stearate (formed from stearic acid and butanol)
The corresponding carboxylic acids and alcohols formed from these esters are:
- Ethyl acetate → Acetic acid + Ethanol
- Methyl salicylate → Salicylic acid + Methanol
- Butyl stearate → Stearic acid + Butanol
Products of Ester Hydrolysis
The two main products formed in ester hydrolysis are:
- Carboxylic acid
- Alcohol
The structural relationship between the ester and its hydrolysis products is as follows:
- The carboxylic acid has the same carbon chain as the ester, but with an -COOH group instead of an -COOR’ group.
- The alcohol has the same carbon chain as the ester, but with an -OH group instead of an -COOR group.
The rate of ester hydrolysis is influenced by several factors, including:
- The nature of the ester (primary, secondary, or tertiary)
- The concentration of water
- The temperature
- The presence of a catalyst (acid or base)
Mechanism of Ester Hydrolysis, Draw the products formed from the ester hydrolysis reaction shown
There are two main mechanisms of ester hydrolysis:
- Acid-catalyzed hydrolysis
- Base-catalyzed hydrolysis
Acid-catalyzed hydrolysis
In acid-catalyzed hydrolysis, a proton from the acid attacks the carbonyl oxygen of the ester, forming a tetrahedral intermediate. This intermediate then collapses to form a carboxylic acid and an alcohol.
The steps involved in acid-catalyzed hydrolysis are as follows:
- Protonation of the carbonyl oxygen
- Nucleophilic attack by water
- Collapse of the tetrahedral intermediate
Base-catalyzed hydrolysis
In base-catalyzed hydrolysis, a hydroxide ion attacks the carbonyl carbon of the ester, forming a tetrahedral intermediate. This intermediate then collapses to form a carboxylic acid and an alcohol.
The steps involved in base-catalyzed hydrolysis are as follows:
- Nucleophilic attack by hydroxide ion
- Collapse of the tetrahedral intermediate
Acid-catalyzed hydrolysis is typically faster than base-catalyzed hydrolysis.
Applications of Ester Hydrolysis
Ester hydrolysis has a wide range of applications in various industries, including:
- Food and beverage production: Ester hydrolysis is used to produce various flavors, fragrances, and emulsifiers used in food and beverages.
- Pharmaceutical manufacturing: Ester hydrolysis is used to produce a variety of drugs and drug intermediates.
- Textile processing: Ester hydrolysis is used to remove sizing agents from textiles and to improve the dyeing and finishing properties of fabrics.
Specific examples of how ester hydrolysis is used in these applications include:
- The production of ethyl acetate, which is used as a solvent and flavoring agent in the food and beverage industry.
- The production of aspirin, which is a pain reliever and fever reducer.
- The removal of sizing agents from cotton fabrics, which improves their ability to absorb dyes and finishes.
FAQ Section
What are the main products of ester hydrolysis?
The main products of ester hydrolysis are carboxylic acids and alcohols.
What are the two main mechanisms of ester hydrolysis?
The two main mechanisms of ester hydrolysis are acid-catalyzed and base-catalyzed.
What factors influence the rate of ester hydrolysis?
Factors that influence the rate of ester hydrolysis include temperature, pH, and the nature of the ester and catalyst.