Mcgee model ap human geography – The McGee Model, a cornerstone in AP Human Geography, unveils the intricate tapestry of spatial relationships that shape our world. Its innovative framework empowers us to decipher the dynamic interplay between people and their environments, revealing the captivating patterns and processes that define our planet.
This comprehensive guide delves into the theoretical underpinnings, components, and applications of the McGee Model. We’ll explore its historical evolution, examine its strengths and limitations, and compare it to other spatial models. Along the way, case studies and examples will illuminate the practical implications of this groundbreaking model.
Historical Context
The McGee Model emerged in the field of AP Human Geography as a framework for understanding the spatial patterns and processes associated with human populations. Its development was influenced by the work of several key individuals, including:
Griffith Taylor
* Australian geographer who proposed the concept of “environmental determinism,” which emphasizes the influence of physical factors on human behavior and culture.
Ellen Churchill Semple
* American geographer who expanded on Taylor’s ideas, arguing that physical factors shape not only human behavior but also social and economic institutions.
Isaiah Bowman
* American geographer who developed the concept of “geographic determinism,” which asserts that physical factors determine the distribution and development of human populations.
Derwent Whittlesey
* American geographer who coined the term “McGee Model” in 1951, recognizing the contributions of WJ McGee to the field of human geography.
WJ McGee
* American geologist and anthropologist who proposed the concept of “culture zones,” which suggested that human populations adapt to their physical environment in different ways, resulting in distinct cultural regions.These individuals, among others, laid the foundation for the McGee Model, which continues to be used as a valuable tool for analyzing human-environment interactions in AP Human Geography.
Theoretical Framework
The McGee Model draws upon several key theoretical concepts from the field of geography. These include:
Spatial interdependencerefers to the interconnectedness of places and the ways in which events and processes in one location can have ripple effects on other locations. For example, a natural disaster in one region can disrupt supply chains and economic activity in other regions.
Spatial diffusionrefers to the spread of ideas, innovations, and other phenomena from one place to another. This can occur through a variety of mechanisms, such as migration, trade, and the media. For example, the spread of new technologies from urban centers to rural areas is an example of spatial diffusion.
Spatial interactionrefers to the interactions between people and places. These interactions can take many forms, such as trade, travel, and communication. For example, the flow of goods and services between different regions is an example of spatial interaction.
These concepts provide the foundation for the McGee Model, which seeks to explain the spatial distribution of economic activity and other phenomena.
Components and Structure
The McGee Model is a comprehensive framework that examines the spatial organization of human activity. It comprises several core concepts and variables that interact to shape the distribution and patterns of human activities across space.The model’s hierarchical structure represents different levels of spatial organization, ranging from the micro-level (individual behavior) to the macro-level (global patterns).
This hierarchical approach allows for a comprehensive understanding of how human activities are influenced by factors operating at various scales.
Core Concepts
The McGee Model revolves around several key concepts, including:
-
-*Space
The physical and social environment in which human activities occur.
-*Activity
Any form of human behavior that utilizes space.
-*Interaction
The connections and relationships between different activities and locations.
-*Organization
The spatial arrangement of activities and interactions, creating patterns and structures.
Variables
The model also incorporates a range of variables that influence the spatial organization of human activity. These variables include:
-
-*Distance
The physical separation between locations.
-*Accessibility
The ease of movement between locations.
-*Land use
The allocation of land for different purposes.
-*Transportation
The infrastructure that facilitates movement between locations.
-*Technology
The tools and techniques used to overcome spatial barriers.
Hierarchical Structure
The McGee Model is organized into a hierarchical structure, with each level representing a different scale of spatial organization. The hierarchical levels include:
-
-*Micro-level
Individual behavior and interactions within a small area.
-*Meso-level
The McGee model in AP Human Geography provides a comprehensive framework for understanding the spatial patterns and processes that shape our world. Its six elements—environment, society, culture, politics, economics, and technology—can be used to analyze a wide range of issues, from the response to an imam crossword to the global refugee crisis.
By examining the interconnections between these elements, the McGee model helps us to develop a deeper understanding of the complex challenges facing our planet.
Interactions and patterns within a region or city.
-*Macro-level
Global patterns and interactions across large geographic areas.
This hierarchical structure allows for a comprehensive understanding of how human activities are influenced by factors operating at various scales. It also highlights the interconnectedness of human activities across different levels of spatial organization.
Applications in AP Human Geography
The McGee Model has proven valuable in AP Human Geography, providing a comprehensive framework for analyzing and understanding a wide range of geographical phenomena.One notable application is in the study of*population geography. The model’s emphasis on spatial patterns, mobility, and population change allows students to explore the distribution, density, and dynamics of human populations.
For instance, the McGee Model can be used to analyze population pyramids, migration patterns, and the impact of urbanization on population dynamics.The McGee Model also finds application in*cultural geography. Its focus on human-environment interactions highlights the ways in which culture shapes the landscape and vice versa.
Students can use the model to examine the spatial distribution of cultural traits, such as language, religion, and ethnicity, and explore how these traits influence social and economic development.Furthermore, the McGee Model is useful in*economic geography. By considering the spatial organization of economic activities, the model helps students understand the factors that drive economic growth and development.
It can be used to analyze the distribution of industries, the role of transportation networks, and the impact of globalization on economic landscapes.
Strengths and Limitations
While the McGee Model provides a valuable framework for understanding human geography, it also has certain limitations. One limitation is that the model focuses primarily on the physical environment and its influence on human activities. While this is an important factor, it may not fully capture the complexity of human decision-making and the role of social and cultural factors in shaping the landscape.Another
limitation is that the McGee Model can be difficult to apply to specific case studies. The model provides a general framework, but it may require adaptation and modification to be effectively used in different contexts.Despite these limitations, the McGee Model remains a valuable tool for AP Human Geography students.
It provides a comprehensive framework for understanding the spatial organization of human activities and can be applied to a wide range of topics within the discipline.
Criticisms and Refinements
The McGee Model has been criticized for several reasons. First, it has been argued that the model is too simplistic and does not take into account the complexity of human behavior. Second, the model has been criticized for being deterministic, meaning that it assumes that environmental factors are the only factors that influence human behavior.
Third, the model has been criticized for being static, meaning that it does not take into account the changing nature of the environment and human society.
In response to these criticisms, the McGee Model has been refined and updated over time. The most recent version of the model, known as the McGee-Robbins Model, takes into account the complexity of human behavior, the role of non-environmental factors, and the changing nature of the environment and human society.
Criticisms, Mcgee model ap human geography
One of the main criticisms of the McGee Model is that it is too simplistic. The model assumes that environmental factors are the only factors that influence human behavior. However, this is not always the case. Human behavior is also influenced by cultural, social, economic, and political factors.
Another criticism of the McGee Model is that it is deterministic. The model assumes that environmental factors determine human behavior. However, this is not always the case. Humans have the ability to make choices and to adapt to their environment.
Finally, the McGee Model has been criticized for being static. The model assumes that the environment and human society are unchanging. However, this is not the case. The environment and human society are constantly changing.
Refinements
In response to these criticisms, the McGee Model has been refined and updated over time. The most recent version of the model, known as the McGee-Robbins Model, takes into account the complexity of human behavior, the role of non-environmental factors, and the changing nature of the environment and human society.
The McGee-Robbins Model is a more complex and nuanced model than the original McGee Model. It takes into account a wider range of factors that influence human behavior, including cultural, social, economic, and political factors. The model also recognizes that the environment and human society are constantly changing.
The McGee-Robbins Model has been used to explain a wide range of human behaviors, including migration, land use, and economic development. The model has also been used to develop policies to address environmental problems.
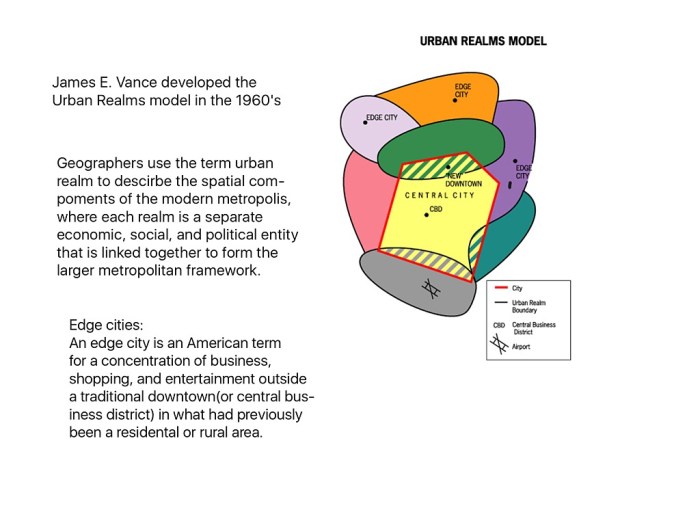
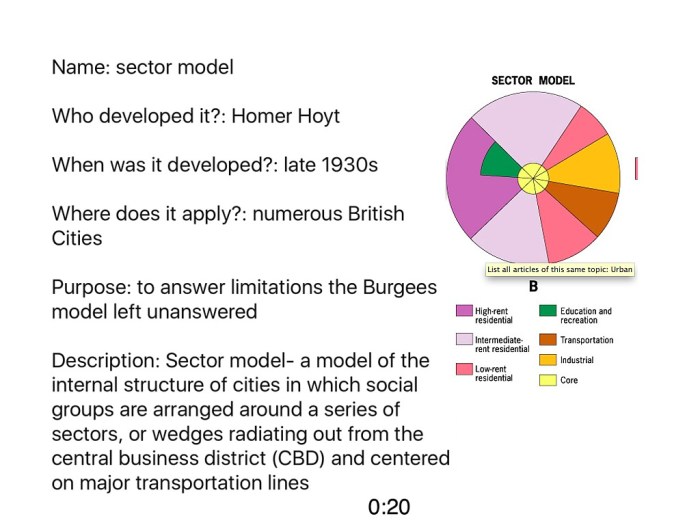
Comparison to Other Models
The McGee Model is not the only spatial model used in AP Human Geography. Other notable models include the von Thünen Model, the Central Place Theory, and the Gravity Model. Each model has its own unique strengths and weaknesses, and they are all used to explain different aspects of human geography.
One of the key similarities between the McGee Model and other spatial models is that they all use distance as a key factor in explaining the distribution of human activities. However, the McGee Model is unique in that it also takes into account the role of transportation costs.
This makes the McGee Model more useful for explaining the distribution of economic activities, such as the location of factories and businesses.
von Thünen Model
The von Thünen Model is a spatial model that explains the distribution of agricultural activities. It is based on the assumption that farmers will choose to locate their farms as close to the market as possible, while taking into account the costs of transportation.
The von Thünen Model predicts that the distribution of agricultural activities will be concentric, with the most intensive activities located closest to the market and the least intensive activities located farthest from the market.
Central Place Theory
The Central Place Theory is a spatial model that explains the distribution of urban settlements. It is based on the assumption that people will choose to live in the largest settlement that is within a reasonable distance of their workplace.
The Central Place Theory predicts that the distribution of urban settlements will be hierarchical, with the largest settlements located at the center of the hierarchy and the smallest settlements located at the periphery.
Gravity Model
The Gravity Model is a spatial model that explains the interaction between two or more locations. It is based on the assumption that the interaction between two locations will be proportional to the size of the two locations and inversely proportional to the distance between them.
The Gravity Model is used to explain a variety of interactions, such as the flow of goods and services, the movement of people, and the spread of ideas.
Case Studies and Examples
The McGee Model has been applied in various regions to understand spatial patterns and processes. Here are a few case studies that illustrate its practical application:
One notable case study is the analysis of land-use patterns in the United States. The model was used to explain the historical evolution of land-use patterns, from the initial settlement of the country to the present day. The study revealed that the distribution of land use in the United States has been shaped by a combination of physical, economic, and social factors.
Urbanization in Southeast Asia
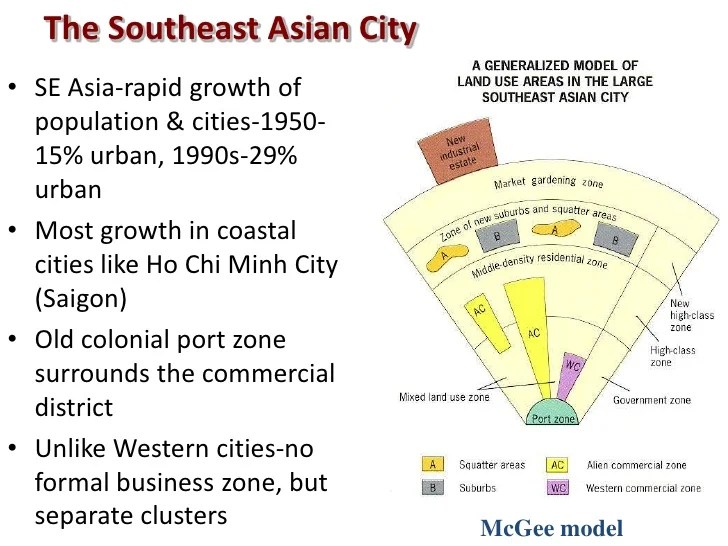
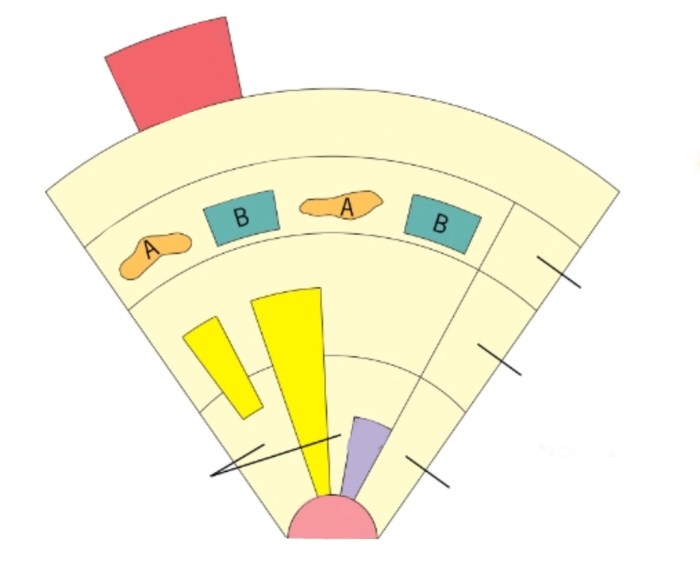
Another case study that demonstrates the application of the McGee Model is the study of urbanization in Southeast Asia. The model was used to explain the rapid urbanization that has occurred in the region in recent decades. The study found that the urbanization process in Southeast Asia has been driven by a combination of economic, social, and political factors.
Conclusion
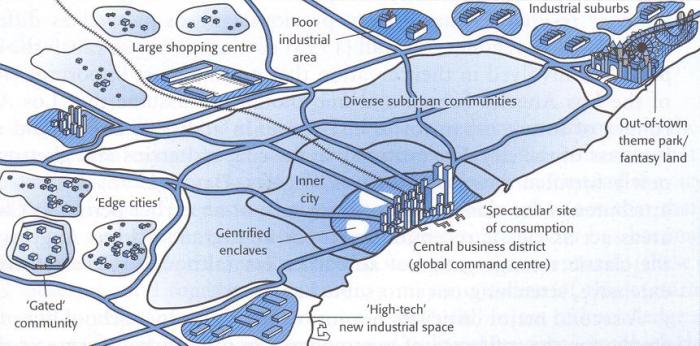
The McGee Model has provided a valuable framework for understanding the complex interactions between humans and their environment in AP Human Geography. It highlights the importance of considering the historical, theoretical, and spatial dimensions of human-environment relationships.
The model’s emphasis on scale, place, and interconnectedness has helped geographers to analyze a wide range of human activities, from local land use decisions to global environmental challenges. It has also fostered interdisciplinary research and collaboration, as it encourages scholars to draw upon insights from other fields such as history, sociology, and ecology.
Clarifying Questions: Mcgee Model Ap Human Geography
What is the key concept behind the McGee Model?
The McGee Model emphasizes the interconnectedness of space and the flow of people, ideas, and goods across different regions.
How is the McGee Model structured?
The model consists of a hierarchical framework that represents different levels of spatial organization, from local to global.
What are the strengths of the McGee Model?
The model’s strength lies in its ability to capture the dynamic interactions between human activities and the physical environment.
What are the limitations of the McGee Model?
The model can be complex to apply and may not always account for the full range of factors that influence human geography.
How has the McGee Model been refined over time?
The model has undergone several refinements to address criticisms and incorporate new research findings.
